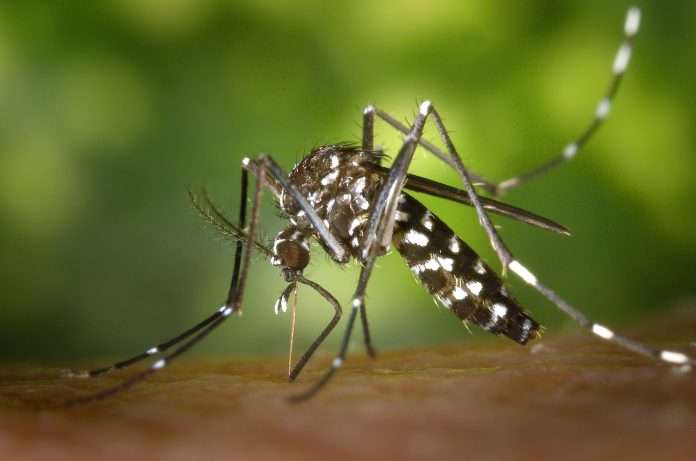
Dengue fever is agonizing and devitalizing. The dengue virus is a mosquito-borne ailment that causes weakness. The viruses causing Yellow fever and West Nile infection are related to Dengue viruses. Dengue Fever Symptoms include rashes, headaches, high fevers, and pain spread out over the entire body. Although the pain associated with dengue is intense, the disease is usually not fatal. Most people suffering from dengue feel better after two or three days, and may completely recover within two weeks.
Dengue fever can be commonly found in subtropical and tropical climates. It’s a huge issue in Southeast Asia and some Latin American countries. Dengue fever is not that common in the US, only found amongst people who bring it with them while traveling from other countries.
Table of Contents
How it began to spread
The name dengue originated from a Swahili phrase which referred to seizures accompanying cramps. They believed these seizures were the works of evil spirits. Spanish “dengue” may have influenced the Swahili term “dinga”. The Spanish term “dengue” means assiduous, describing the way someone plagued by bone pain caused by dengue fever walks. It is possible that the Spanish term was influenced by Swahili. West Indian slaves who contracted this disease walked in this manner, carefully like a person overly concerned with their appearance or a “dandy”. For this reason, “Dandy Fever” was the name given to the disease.
The First Signs of Dengue can be found in ancient China. A medical encyclopaedia belonging to the Jin Dynasty tells about a poison originating in the water and carried by mosquitoes. Between the 15th century, and the 19th century, aegypti, which is the primary carrier, expanded out of Africa. In the 17th century, there have been reports of dengue fever escalating to epidemics, but the earliest verifiable report of dengue epidemics can be found in 1779, when an outbreak spread across Asia, North America, and Africa.
Confirmation
In 1906, it was confirmed that dengue was spread by Aedes Aegypti mosquitoes. Yellow fever was the first disease originating from a virus, and the second one was dengue. After further investigation, scientists finally understood how dengue was transmitted. Since the Second World War, there has been mass ecological disruption which has contributed to the disease spreading further.
Different versions of dengue spread to untouched areas due to the same reason and eventually caused dengue hemorrhagic fever to emerge. In 1953 Phillipines, dengue hemorrhagic fever was reported for the first time, and by the time the 1970s began, it spread to the Pacific region and America. Dengue Symptoms In Child were noted, and the disease was one of the chief causes of child mortality. In South and Central America, the disease was first noted in 1981.
How is Dengue Transmitted
Dengue viruses are transmitted to humans via the female Aedes mosquitoes. Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus are the two species of mosquitoes that can also transmit other mosquito-borne viruses, including zika and chikungunya. It can also spread from an infected mother to her fetus. There is no evidence of it spreading through breastfeeding or sexual contact. In some rare cases, the virus is transmitted via blood transfusions from infected donors.
Mosquitoes obtain the virus while sucking the blood of a person already infected with dengue. After an incubation period of eight to ten days, the mosquito is able to transmit the virus for the rest of its life. There is no way to determine if a mosquito is carrying the dengue virus or not. It is possible that an infected mosquito can transfer the virus to its offspring via the eggs, but whether this offspring can transfer the disease to humans, is not yet known.
Infected humans serve as the main source of the virus. They are the main carriers and uninfected mosquitoes get infected when they bite an infected human. The virus flows in the blood of the infected human for two to seven days, and at the same moment, they catch a fever and Dengue Fever Symptoms can be seen. This is the time period during which Aedes mosquitoes may obtain the virus when they feed on that infected human. In parts of South East Asia and Africa, apes in the jungle may play a part in the transmission.
What you need to know
The Aedes mosquito breeds in stagnant water, often close to human habitat. They prefer dark places under furniture, dim-lit bathrooms, etc. They may also love in pools of water where human waste is collected. Also, they are most active during the daytime, especially at dawn. A dengue epidemic occurs when the virus is introduced in a region where there are a large number of susceptible adults and children.
Hyper-endemic dengue transmission can occur when multiple viral serotypes are distributed in an area where a large pool of susceptible hosts and a suitable vector are always present. This is how dengue is globally transmitted. Antibody presence increases with age and most adults in the population are immune. Hyper-endemic transmission is one of the main causes of Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever.
The chances of infection are 25-50%. Dengue has recently surfaced in parts of Asia, Africa, and South America and has spread rapidly. Efforts are being made by the respective government and independent organizations to raise awareness and control the spread of this virus.
Dengue Facts
Some of the facts related to Dengue are:
- Dengue may be life-threatening, and in severe cases, may require the patient to be hospitalized
- An estimated 400 million dengue infections occur worldwide each year, with about 96 million resulting in illness.
- Less than 5% of cases are severe, and only a tiny percentage of these may prove to be fatal. Children are more susceptible to severe cases of dengue and even fatalities. This severe form of dengue,known as Dengue hemorrhagic fever, along with Dengue Fever Symptoms can cause thevascular permeability to increase, in turn leading to hypovolemic shock that may be fatal.
- The areas in which this disease is most prevalent include the Southern China, Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Taiwan, The Caribbean (except Cuba and the Cayman Islands), The Pacific Islands, Mexico, Africa, and South and Central America
Symptoms
Mild symptoms of dengue include fever, aches, and pains, or Dengue Fever Rash. The most common Dengue Fever Symptoms include severe headaches, pain felt at the region behind the eyes, severe joint and muscle pain, fatigue, nose or gum bleeding. Some symptoms are generic and can be mistaken for those of flu. People with weak immune systems, especially children are most vulnerable to these.
A more severe variety of dengue, the Dengue hemorrhagic fever causes Dengue Fever Symptoms such as bleeding from the mouth, gums or nose, damaged lymph and blood vessels, internal bleeding leading to black vomit and stool, pulse weakening, blood spots under the skin, decrease in the number of blood platelets, etc.
Dengue shock syndrome is another severe form of dengue. The symptoms of this disease include stomach pain, heavy bleeding, vomiting, a sudden fall in blood pressure, disorientation, and hypo-tension.
When Should You Seek Treatment
It is advisable to consult a doctor immediately if you are displaying Dengue Fever Symptoms. You should consult a doctor if you are showing symptoms after visiting a region where there is an outbreak of the virus. The doctor will ask you basic questions about your well-being, what discomforts you are experiencing and where you have traveled to recently. You may be required to undertake a blood sample test.
Often the fever would go down after a few days of Dengue Fever Symptoms showing. This is an ideal time to get yourself checked into a hospital to seek treatment. Neglecting the disease can prove to be fatal and one should seek treatment as early as possible in order to get better.
How to diagnose dengue
RT-PCR can detect dengue in the bloodstream. Depending upon the serotype, non-structural dengue antigen can be detected in the bloodstream. The virus may be isolated for research purposes. In the case of an outbreak, authorities need to determine the genotype and serotype of the disease. Dengue IgM antibodies can be detected in serum specimens to determine the serotype.
In the case of a dengue infection, the antibodies called Dengue Igm appear 2-3 days after the onset of infection and are short-lasting. Cross-sections of the serological nature may exist between the virus carrying dengue and flaviviruses closely related to it.
Prevention
The only way of preventing dengue is avoiding mosquito bites. No vaccine has been developed to offer protection against Dengue Fever Symptoms. Some of the ways we can prevent dengue include:
- Reduce skin exposure. Wear long-sleeved clothes, long pants, and socks. Hats can be worn to protect the head.
- Use repellents but exercise caution.
- Use mosquito nets at night while sleeping.
- Window screens and nets can keep the mosquitoes out.
- Avoid using strong perfumes as they might attract mosquitoes.
- Get rid of stagnant water around you on a regular basis. Drain plant pots, and make sure no water accumulates in buckets or other containers. Change the water in flower vases every day. Ensure that drains are not blocked. Do not place receptacles under air conditioning machines.
- While out for camping, choose a spot that is away from water.
Treatment
There is no one drug that can cure dengue fever. Patients should get rest and drink a lot of water. Paracetamol can reduce fever and joint pains. Already infected Patients can cause the disease to spread further, and thus, they should sleep inside mosquito nets. Once a person has been infected by a particular strain, that strain can never affect them again. But other strains can still infect them.
When Dengue Fever Symptoms are present, a doctor must be consulted and you must get yourself admitted to a hospital. Case-fatality rates are below 1% when dealt with proper care and timing. However, the overall experience is extremely unpleasant and painful. In more severe cases, the treatment includes fluid therapy.
The fluid is usually administered orally. In case the patient is unable to take fluid orally due to severe vomiting, prostration or shock, it may be administered intravenously. The aim is to keep enough fluid in the vascular system to prevent hypovolemia. For intravenous treatment, crystalloids (0.9% saline) is used.
The rate of fluid administration varies according to the situation. If the patient goes into shock, 20 mL/kg boluses should be used for resuscitation. The fluid quota should be calculated for the entire period. Colloids like dextran should be administered as a secondary therapy when hypotension is not responding to boluses of intravenous crystalloids.
Further hemoconcentration due to leakage may cause a rise in hematocrit, increasing the demand for fluids. However, a drop in hematocrit may be due to re-absorption of fluid or internal bleeding. If the platelet count is low, there may be bleeding. In such cases, a blood transfusion may be required.
Control Strategies
A widespread outbreak of dengue demands control strategies to prevent it from turning into a mass epidemic. GIS mapping can be used to locate dengue concentrations. By locating dengue cases within the affected area, treatment can proceed with various preventive strategies. Moreover, GIS mapping allows better surveillance and can determine the breeding ground for mosquitoes.
Surveillance provides risk assessment, outbreak reaction, program evaluation, and guidance. It allows timely response and establishment of control strategies. On the other hand, these programs do not focus on the elimination of the virus. The eruption of dengue in Singapore in 2009 was caused due to excessive control measures and inefficient surveillance. Further, by gaining knowledge regarding vector concentration and its breeding, we can effectively control the disease.
Aegypti females lay eggs above the stagnant water in containers or jars and so on for their survival. It is crucial to determine the behavior pattern of vectors to effectively locate these egg-laying sites. Once the oviposition sites have been determined, effective strategies can be employed for the elimination of the mosquitoes at that site.
Community-based programs are arranged to make the public aware of the disease and the breeding sites of mosquitoes. When people are aware of the disease, about Dengue Fever Symptoms and how it spreads, the likeliness of an outbreak occurring significantly decreases.